Addition of ATP to midazolam offers enhanced dental sedation, fewer adverse effects
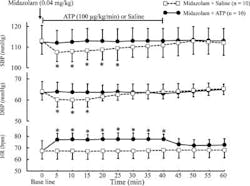
BIS analyzes electroencephalogram (EEG) patterns to continuously assess the depth of sedation. The patients’ consciousness was evaluated by their response to verbal commands such as “squeeze my fingers” and “open your eyes.” These parameters showed a deeper level of sedation for the use of midazolam plus ATP. Under midazolam alone, patients showed a BIS value that went from 97 (±1) prior to administration to 68 (±18) after 25 minutes. The volunteers remained conscious, but showed signs of significant cardiopulmonary depressant effects. However, following 15 to 30 minutes of coadministration of ATP, no adverse cardiorespiratory effects were seen and patients became unconscious. The BIS value further reduced to 51 (±13) after receiving ATP. No adverse effects such as hypotension, chest pains, headache, nausea, or vomiting were seen. The authors conclude that the addition of ATP significantly enhances the sedation effect of midazolam with improved cardiorespiratory functions. Full text of “IV ATP Potentiates Midazolam Sedation as Assessed by Bispectral Index,” Anesthesia Progress, Vol. 61, No. 3, 2014, is available here. For more information about Anesthesia Progress, visit their website.